题面
At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite sequence of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers how to repair the sequence. Initially he should create an integer array a[1], a[2], ..., a[n]. Then he should perform a sequence of m operations. An operation can be one of the following:
- Print operation l, r. Picks should write down the value of
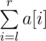 .
. - Modulo operation l, r, x. Picks should perform assignment a[i] = a[i] mod x for each i (l ≤ i ≤ r).
- Set operation k, x. Picks should set the value of a[k] to x (in other words perform an assignment a[k] = x).
Can you help Picks to perform the whole sequence of operations?
The first line of input contains two integer: n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105). The second line contains n integers, separated by space: a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) — initial value of array elements.
Each of the next m lines begins with a number type 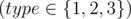 .
.
- If type = 1, there will be two integers more in the line: l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n), which correspond the operation 1.
- If type = 2, there will be three integers more in the line: l, r, x (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 2.
- If type = 3, there will be two integers more in the line: k, x (1 ≤ k ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 3.
For each operation 1, please print a line containing the answer. Notice that the answer may exceed the 32-bit integer.
5 5 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 5 4 3 3 5 1 2 5 2 1 3 3 1 1 3
8 5
10 10 6 9 6 7 6 1 10 10 9 5 1 3 9 2 7 10 9 2 5 10 8 1 4 7 3 3 7 2 7 9 9 1 2 4 1 6 6 1 5 9 3 1 10
49 15 23 1 9
Consider the first testcase:
- At first, a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}.
- After operation 1, a = {1, 2, 3, 0, 1}.
- After operation 2, a = {1, 2, 5, 0, 1}.
- At operation 3, 2 + 5 + 0 + 1 = 8.
- After operation 4, a = {1, 2, 2, 0, 1}.
- At operation 5, 1 + 2 + 2 = 5.
简洁的题目翻译(取自luogu)
给定数列,区间查询和,区间取模,单点修改。
n,m小于10^5
题解
相当裸的一道线段树,但是思路相当神奇
首先我们会注意到,这题有要求区间修改和区间查询,学过线段树的神犇们可能就立刻会想到一系列诸如标记永久化,打lazytag等一系列高端操作来维护这颗线段树
但是实际上不用这样做哒qwq
否则你可能会像本蒟蒻一样在这道题上卡了一个半小时还一分都拿不到
因为这道题实际上是区间取模,取模实际上没办法像加法乘法一样做到利用一些lazytag的奇怪的做法把复杂度压成O(nlogn)
那么怎么做呢?
第四句话给了提示qwq
就是对要取模的区间暴力单点修改就行
这时候就有人要问了,这样暴力复杂度不对吧,当然不能,所以我们需要加一些玄学优化
首先我们要证明一些奇怪的东西
引理1:对一个数取模,如果能够取模,那么这个数至少会变成原来的\( \frac{1}{2} \),这非常的显然,所以我就懒得证明了23333
还是简单的证明一下,如果一个数能够被取模,则取模后它一定会变成小于模数的形式,如果模数大于原数的\( \frac {1}{2} \)则取模后结果一定会小于原数减去模数即结果一定小于原数的\( \frac {1}{2} \) ,现在考虑另一种情况,若模数小于原数的\( \frac {1}{2} \),则取模后的结果一定会小于模数,即结果一定小于等于原数的\( \frac {1}{2} \)
所以现在得证,一个数取模后规模至少缩小\( \frac{1}{2} \)
然后我们继续证明一些性质
引理2:若一个数被取模,则至多取模\( \lg N \)次
由引理1可知,一个数每次被取模规模都会缩小\( \frac{1}{2}\),所以只需要取模\( \lg N \)次就不可以继续取模了
现在有了这两个性质,我们再进行一些合理的猜想
取模运算很慢,那么为了减少运行时间,我们在能够不取模的时候应当不取模
引理3:若一个数小于模数,那么这个数取模后的结果和原数相等
显然,根据模除的性质,若这个数小于模数,那么除法运算最后的余数一定与原数相等
既然可能相等,我们就在出现相等情况时不取模就好了
因此,我们再在区间和之外多维护一个区间最大值即可,当模数大于区间最大值时,不对这个区间进行取模操作
下面就可以进行复杂度证明了
复杂度:O(nlogn)
证明:总共有n个数,因为一旦取模后结果可能不变就不会继续取模,所以每个数最多被取模\( \lg N \)次,所以最终的取模次数最多为nlogn次,时间复杂度为O(nlogn)
证毕
单点修改没什么好说的,现在我们就可以任性的取模了
贴代码
#include#include #include using namespace std;const int MAXN = 100100;long long maxm[MAXN<<2],sum[MAXN<<2],a[MAXN];long long n,m;void pushup(long long o){ maxm[o]=max(maxm[o<<1],maxm[o<<1|1]); sum[o]=(sum[o<<1]+sum[o<<1|1]);}void build(long long l,long long r,long long o){ if(l==r){ sum[o]=a[l]; maxm[o]=a[l]; return; } long long mid=(l+r)>>1; build(l,mid,o<<1); build(mid+1,r,o<<1|1); pushup(o);}void updateadd(long long pos,long long l,long long r,long long o,long long v){ if(l==r){ sum[o]=v; maxm[o]=v; return; } long long mid=(l+r)>>1; if(pos<=mid) updateadd(pos,l,mid,o<<1,v); else updateadd(pos,mid+1,r,o<<1|1,v); pushup(o);}void updatemod(long long pos,long long l,long long r,long long o,long long v){ if(l==r){ sum[o]=sum[o]%v; maxm[o]=maxm[o]%v; } long long mid=(l+r)>>1; if(pos<=mid) updatemod(pos,l,mid,o<<1,v); else updatemod(pos,mid+1,r,o<<1|1,v); pushup(o);}long long query(long long L,long long R,long long l,long long r,long long o){ if(L<=l&&r<=R){ return sum[o]; } long long ans=0,mid=(l+r)>>1; if(L<=mid) ans+=query(L,R,l,mid,o<<1); if(R>mid) ans+=query(L,R,mid+1,r,o<<1|1); return ans;}void update(long long L,long long R,long long l,long long r,long long o,long long v){ if(l==r){ sum[o]=sum[o]%v; maxm[o]=maxm[o]%v; return; } long long mid=(l+r)>>1; if(L<=mid&&maxm[o<<1]>=v) update(L,R,l,mid,o<<1,v); if(R>mid&&maxm[o<<1|1]>=v) update(L,R,mid+1,r,o<<1|1,v); pushup(o); }int main(){ scanf("%lld %lld",&n,&m); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]); build(1,n,1); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ int mode; scanf("%d",&mode); if(mode==1){ long long lx,rx; scanf("%lld %lld",&lx,&rx); printf("%lld\n",query(lx,rx,1,n,1)); } else if(mode==2){ long long lx,rx,x; scanf("%lld %lld %lld",&lx,&rx,&x); update(lx,rx,1,n,1,x); } else{ long long k,x; scanf("%lld %lld",&k,&x); updateadd(k,1,n,1,x); } } return 0;}